Rick's b.log - 2023/01/21
You are 18.116.47.235, pleased to meet you!
Rick's b.log - 2023/01/21 |
|
| It is the 18th of December 2024 You are 18.116.47.235, pleased to meet you! |
|
mailto: blog -at- heyrick -dot- eu
How about if we could look at something like this instead?
It's actually not that hard. But if we're using pure BASIC, kiss goodbye to any hint of a useful redraw speed.
The first thing we need is to have some textures. I have chosen to use a set of 64×64 sprites. These are named a, b, and c to correspond to the three different "colours". The names are suffixed with either x or y depending if it's the brighter one (x) or the dimmer one (y).
The three textures are a brick-like, sort-of concrete, and something that's a bad impression of wood panelling. It took literally ten minutes in Paint to do this. ☺
After allocating memory for the triple buffering, but before setting up the screen and banking, insert this code to load the textures.
Now everything is as normal until we get to the part that selects the colours and draws the lines to the screen. This part:
We're going to replace that with some new code.
It's a little involved, so let's look at it in steps.
The first part works out which texture we want - the first letter being a, b, or c and the second letter being x or y.
Now we need to work out exactly where along the wall the ray has hit. We then subtract this from the integer of itself so we're left with only the part after the decimal point. This tells us how far along the texture we are (a value from 0 to 1).
Now we work out how this maps to pixels in the actual texture, and we also conditionally flip the offset so walls drawn on the opposite side still draw the right way around (otherwise they'd appear back to front).
That's the X offset sorted out. How time to sort out the Y stepping and initial offset. If you're wondering why we don't just set the initial Y offset to zero, the reason is that while this will work for the majority of wall drawing, as soon as you get close to a wall, it'll go wonky.
Now we simply simply step through the individual pixels involved in drawing the line, and pluck out which pixel of the texture to actually plot to the screen.
Doing this with the commented source might get you a single frame per second if you're lucky. Crunching doesn't help. And compiling only helps a little, because you've just dropped in at least thirty thousand SWI calls per redraw (if you're right up against a wall, it's more like three hundred thousand!).
We can do a little better, but this means fiddling with memory directly now.
After this part:
Insert this:
This will read the base address of the current draw screen bank.
Now replace the drawing loop (the read colour, plot pixel) with this:
This does the same thing, but instead of making loads of SWI calls, we only do one to get the base address of the desired sprite, that we then correct to point to the pixel data instead of the sprite header.
The uncompresseed BASIC will run at 4-5fps (on my Pi3B+), going up to 6-7fps for a crunched version. Sadly, it's a lot of fiddly work so this is really stretching BASIC.
The ABC compiler, on the other hand, can maintain around 30fps (and sometimes twice that, no throttling remember?).
Accordingly, this amount of number crunching makes a good use case for the ABC compiler, and given that it is built using VFP instructions, it may well be able to outdo the DDE C compiler!
If you are interested in using the BASIC compiler but don't have the DDE, send an email to David Feugey at
Now, grab the programs (Zip, 14,880 bytes) and begin playing with them.
Potential optimisations:
These optimisations are, of course, up to you.
Ray Casting 3 - wall textures
Looking at coloured walls is okay, but not terribly interesting.
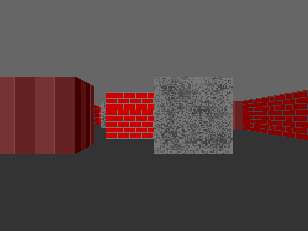
Walls with textures.
![]()
ax![]()
bx![]()
cx![]()
ay![]()
by![]()
cyREM Now load the texture sprites
SYS "XOS_File", 23, "<RayCast3$Dir>.textures" TO ,,,,len% ; f%
IF (f% AND 1) THEN ERROR 123, "Cannot find textures."
len% += 4
DIM texture% len%
texture%!0 = len%
texture%!8 = 16
SYS "OS_SpriteOp", ( 9 + 256), texture%
SYS "OS_SpriteOp", (10 + 256), texture%, "<RayCast3$Dir>.textures"
REM Now work out what colours we want
col% = 127
IF (side% = FALSE) THEN col% += 128
CASE map%(mapx%, mapy%) OF
WHEN 1 : GCOL col%, 0, 0 : REM Red
WHEN 2 : GCOL 0, col%, 0 : REM Green
WHEN 3 : GCOL 0, 0, col% : REM Blue
ENDCASE
REM And, finally, draw the line, with correction between
REM OS units and pixels for MODE 28.
MOVE (scrcol% << 1), (drawbot% << 1)
DRAW (scrcol% << 1), (drawtop% << 1)
REM Which texture are we using?
CASE map%(mapx%, mapy%) OF
WHEN 1 : text$ = "a"
WHEN 2 : text$ = "b"
WHEN 3 : text$ = "c"
ENDCASE
IF (side% = FALSE) THEN
text$ = text$ + "x"
ELSE
text$ = text$ + "y"
ENDIF
REM At this point, we'll have a texture name like
REM "ax" or "by" for which wall type and whether
REM it's an X or Y intersection.
REM Now we need to know where along the wall it was hit
IF ( side% = FALSE) THEN
wallpos = oury + (towall * yray)
ELSE
wallpos = ourx + (towall * xray)
ENDIF
REM Now clip it to be only the offset into the wall piece
wallpos = wallpos - INT(wallpos)
REM Now wallpos is a value from 0 to 1
REM Now work out where this actually is in the texture
textxpos% = wallpos * 64
REM Now flip it if necessary so the opposite sides draw correctly
IF ((side% = FALSE) AND (ydir < 0)) THEN textxpos% = 64 - textxpos% - 1
IF ((side% = TRUE ) AND (xdir > 0)) THEN textxpos% = 64 - textxpos% - 1
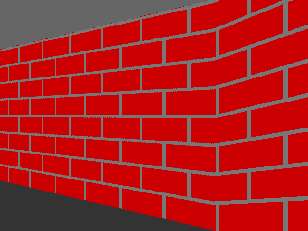
Wonky walls. REM Now we have the X offset sorted, we need to step through
REM the Y for drawing the slice of the textured wall
REM Work out how many pixels we step in the texture for
REM each on-screen pixel
textstep = 1 * (64 / drawsize%)
REM The initial Y offset into the texture
texty = (drawbot% - (height% / 2) + (drawsize% / 2)) * textstep
FOR yloop% = drawbot% TO drawtop%
textypos% = INT(texty) AND 63
REM Read the colour
SYS "OS_SpriteOp", (41 + 256), texture%, text$, textxpos%, textypos% TO ,,,,,c%,t%
REM Plot this pixel
GCOL c% TINT t%
POINT (scrcol% << 1), (yloop% << 1)
texty = texty + textstep
NEXT
Not good.
WHILE TRUE
PROCswitchbank
CLS
screen% = VDU(148)
REM Now get a pointer to the sprite data
SYS "OS_SpriteOp", (24 + 256), texture%, text$ TO ,,address%
address% = address% + address%!32 : REM Pointing to the data now
FOR yloop% = drawbot% TO drawtop%
textypos% = INT(texty) AND 63
col% = address%?( (textypos% * 64) + textxpos% )
screen%?( (yloop% * width%) + scrcol% ) = col%
texty = texty + textstep
NEXT
Then we simply read a byte from the sprite pixel data and write it to the screen memory in the correct position.
This relies upon both the sprite and the screen being 8bpp (or one byte per pixel) and both using the same colour palette.
abc@riscos.fr along with a screenshot of your RISC OS desktop (blank out
any personal information as the screenshots are published on the website).
See https://www.riscosopen.org/forum/forums/1/topics/9003 for more details.
;)
No comments yet...
| © 2023 Rick Murray |
This web page is licenced for your personal, private, non-commercial use only. No automated processing by advertising systems is permitted. RIPA notice: No consent is given for interception of page transmission. |